Artificial Wombs, AI Monitoring, and the Emerging Vision of Ectogenesis
Imagine this for a moment: We all look the way we do today — but there was a time when each of us was nothing more than a microscopic cluster of cells. From a single fertilized cell, we developed into a fully formed human being weighing 3 to 3.5 kilograms at birth.
Now imagine a future where this entire journey — from embryo to newborn — takes place not inside a mother’s body, but inside a laboratory.
This is not just science fiction anymore. It is a serious scientific discussion under the concept known as ectogenesis — the development of a baby outside the human womb.
The Miracle of the Uterus
Human life begins in the uterus, a highly specialized organ designed to support pregnancy for approximately nine months.
For nearly 50 years, scientists have studied the uterus to understand its biological “magic”:
- How does it nourish a fetus?
- How does it regulate oxygen and nutrient supply?
- How does it protect against infection?
- How does it coordinate hormonal balance?
The uterus is not just a container — it is an active biological ecosystem that constantly communicates with the developing fetus.
Modern science has now decoded much of this complex interaction. And that understanding has opened the door to an extraordinary possibility: replicating it artificially.
From IVF to Artificial Gestation
When couples were unable to conceive, society often viewed it as fate. Then science introduced:
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF revolutionized reproductive medicine by allowing fertilization outside the body. However, after fertilization, the embryo is still implanted into the mother’s uterus for development.
Artificial womb technology aims to go one step further — not just fertilization outside the body, but complete gestation outside the body.
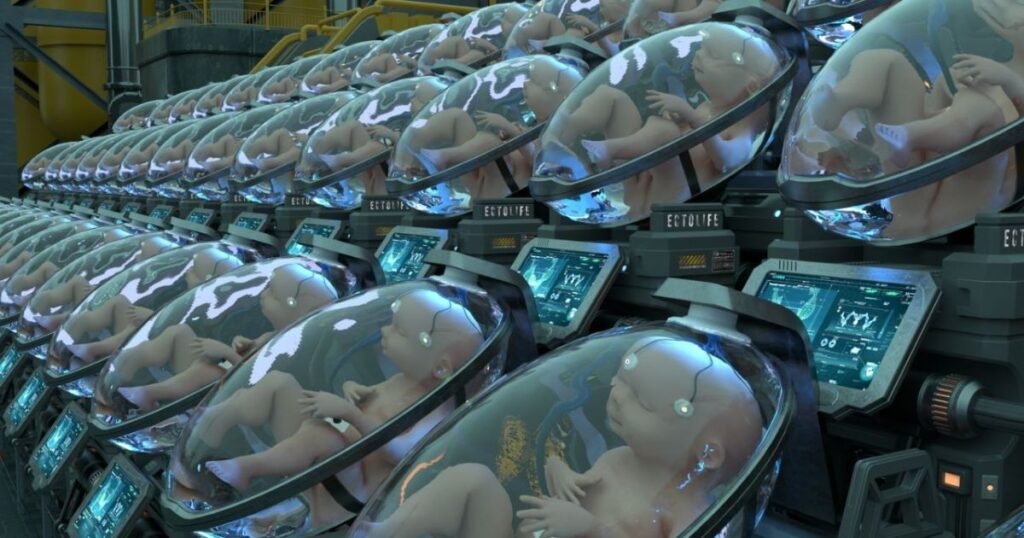
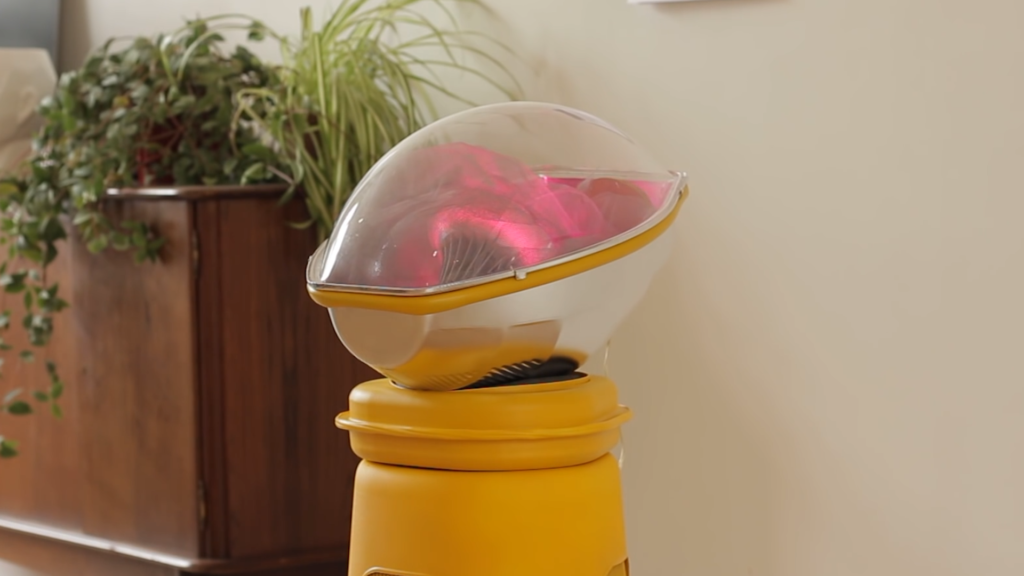
The Concept of ActoLife and Growth Pods
A futuristic project concept called ActoLife proposes a controlled laboratory environment where babies could develop inside advanced “growth pods.”
These pods would:
- Mimic the biochemical environment of the uterus
- Provide oxygen and nutrients through artificial placental systems
- Monitor growth using thousands of sensors
- Use artificial intelligence to analyze fetal health in real time
Imagine a parent sitting at home, wearing a connected device, feeling vibrations that simulate the baby’s movements — while the actual fetus is developing hundreds of kilometers away in a bio-secured lab.
Though still conceptual, parallel scientific developments suggest this future may not be impossible.
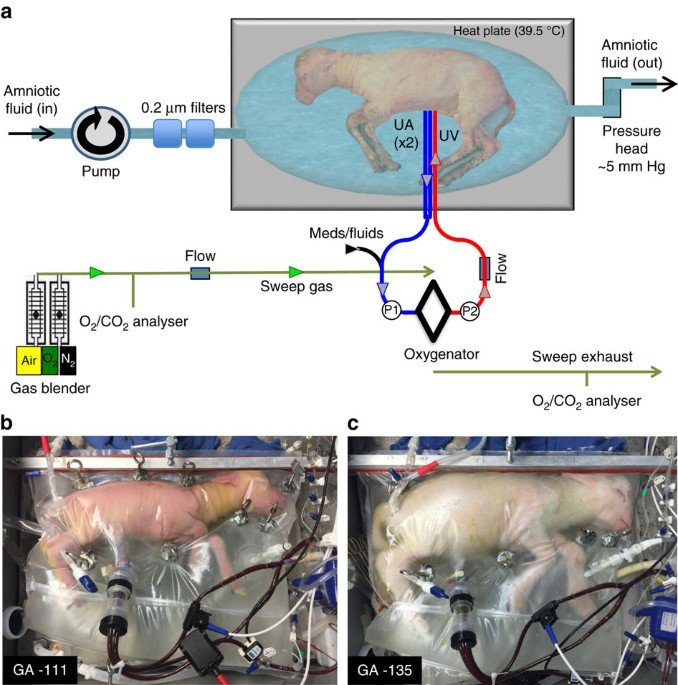
A Real Scientific Breakthrough: BioBag

In 2017, researchers achieved a major milestone with a system known as BioBag.
In this experiment:
- Premature lamb fetuses were placed inside a fluid-filled artificial womb.
- They continued developing for approximately four weeks.
- Their lungs, brain, and organs matured normally.
This was not merely “keeping them alive.” It was active developmental support — essentially simulating the uterine environment.
Subsequent research in different countries has also demonstrated partial artificial gestation in animal embryos.
Human application is still far away — but the foundational science exists.
Why Is Artificial Womb Technology Being Considered?
This concept is not merely futuristic curiosity. It addresses real medical challenges:
- Women born without a functional uterus
- Severe PCOS or uterine disorders
- Uterine cancer survivors
- Repeated pregnancy loss
- High-risk pregnancies
- Complications during C-sections
- Extremely premature births
In such cases, options are often limited to:
- Surrogacy
- Adoption
- Or remaining childless
Artificial gestation could offer a third alternative.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
In a fully developed artificial womb system:
- Thousands of micro-sensors would track fetal heart rate, oxygen levels, metabolism, and cellular development.
- AI algorithms would analyze data continuously.
- Growth irregularities could be detected instantly.
- Nutritional composition could be adjusted in real time.
This could significantly reduce risks associated with:
- Underweight births
- Premature deliveries
- Certain developmental abnormalities
However, it is important to emphasize: science cannot yet guarantee 100% perfect outcomes.
Genetic Screening and Ethical Concerns
Artificial gestation could potentially integrate advanced genetic screening to identify:
- Chromosomal disorders (e.g., Down syndrome)
- Inherited genetic diseases
- Metabolic abnormalities
While this could reduce suffering caused by severe illnesses, it also raises ethical questions:
- Will this lead to “designer babies”?
- Who decides what is considered a “desirable trait”?
- Could inequality increase if only wealthy individuals access such technology?
Declining Birth Rates and Global Demographics
In 2021, Elon Musk publicly expressed concern about declining global birth rates.
Many developed nations are experiencing population shrinkage. If multiple pandemics or global crises occur, maintaining population balance could become a challenge.
Artificial womb technology is sometimes proposed as a long-term demographic solution — though this remains speculative.
The Emotional Question: What About Mother–Child Bonding?
Perhaps the most important debate is not technological — but emotional.
- Will the mother–child bond change?
- Does physical pregnancy shape emotional attachment?
- Can bonding be replicated through virtual or sensory systems?
Some argue that attachment forms after birth through care and interaction. Others believe pregnancy itself creates a unique biological and psychological connection.
This question remains open.
Is This a Change — or a Leap?
Artificial womb technology would not simply be an innovation.
It would be a biological revolution — potentially redefining reproduction, parenthood, and even the meaning of motherhood.
Today, it may sound like science fiction.
But so did:
- Artificial intelligence
- Internet video calls
- Organ transplantation
- IVF
Many technologies once imagined have become everyday realities.
We Got This
Artificial gestation is still in development and surrounded by scientific, ethical, and social challenges. But the foundation has been laid.
If successful, it could:
- Prevent premature infant deaths
- Help infertile couples
- Reduce high-risk pregnancy complications
- Change demographic patterns
At the same time, it could redefine human reproduction in ways we are only beginning to understand.
What Do You Think?
Would laboratory gestation be a blessing for humanity — or a step too far from nature?
Share your detailed thoughts. The future of human reproduction may depend not only on science, but also on society’s decision. Join us in our WhatsApp Group Now or visit our WhatsApp channel below.
- Will Babies Be Born in Laboratories in the Future?
 Artificial Wombs, AI Monitoring, and the Emerging Vision of Ectogenesis… Read more: Will Babies Be Born in Laboratories in the Future?
Artificial Wombs, AI Monitoring, and the Emerging Vision of Ectogenesis… Read more: Will Babies Be Born in Laboratories in the Future? - India’s Engineering Education Paradox (2019–2025)
 Degrees in Abundance, Employability in Crisis — and the Urgent… Read more: India’s Engineering Education Paradox (2019–2025)
Degrees in Abundance, Employability in Crisis — and the Urgent… Read more: India’s Engineering Education Paradox (2019–2025) - 5 Proven Ways to Improve Your Memory – Backed by Neuroscience
 Memory is one of the most fascinating functions of the… Read more: 5 Proven Ways to Improve Your Memory – Backed by Neuroscience
Memory is one of the most fascinating functions of the… Read more: 5 Proven Ways to Improve Your Memory – Backed by Neuroscience - Boost Your Memory FAST with These 4 Brain Secrets!
 Neuroscience isn’t just for scientists in labs—it’s for everyone who… Read more: Boost Your Memory FAST with These 4 Brain Secrets!
Neuroscience isn’t just for scientists in labs—it’s for everyone who… Read more: Boost Your Memory FAST with These 4 Brain Secrets! - The Art of Ignoring: 8 Powerful Ways to Attain Success and Inner Peace
 Introduction: Chanakya’s Timeless Wisdom आचार्य चाणक्य (Acharya Chanakya), in his… Read more: The Art of Ignoring: 8 Powerful Ways to Attain Success and Inner Peace
Introduction: Chanakya’s Timeless Wisdom आचार्य चाणक्य (Acharya Chanakya), in his… Read more: The Art of Ignoring: 8 Powerful Ways to Attain Success and Inner Peace